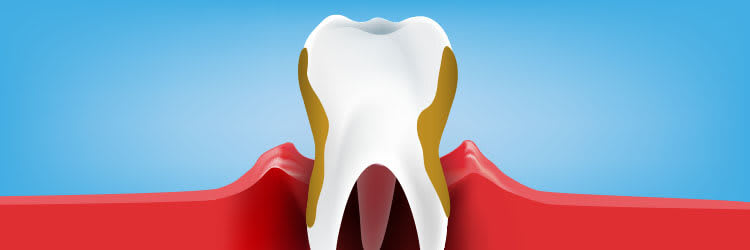
Gum recession is when the margin of the gum tissue surrounding the teeth wears away, or pulls back, exposing more of the tooth, or the tooth's root. When gums recede, gaps can form between the gum and tooth, allowing disease-causing bacteria to build up. If left untreated, the surrounding tissue and bone structures of the teeth can be damaged, sometimes resulting in tooth loss. Receding gums is a widespread dental condition. Most people aren’t aware that they have receding gums since it occurs gradually.
Receding Gums Symptoms
As receding gums progress over time, you may notice the following symptoms:
Long Teeth
One symptom is the visible lengthening of the teeth. When gums recede because of periodontal disease, the teeth have the appearance of being much longer than normal.
Exposed Roots
Exposed roots are another symptom, and can be extremely sensitive and uncomfortable. They are often a sign of periodontal disease or can be attributed to brushing overly aggressively with a toothbrush with hard bristles.
Loose teeth
When suffering from receding gums, you may notice loose teeth, attributed to the bacteria and periodontal disease under the gums around the teeth. As receding gums worsen, the gum pockets deepen due to loss of attachment structure.
Causes of Receding Gums
Numerous factors can cause your gums to recede, including:
Periodontal diseases
These are gum infections, caused by bacteria, that destroy gum tissue and the bone that holds your teeth in place. Periodontal disease is the main cause of gum recession. The early stage of periodontal disease is not often painful, therefore symptoms often go unnoticed. Left untreated though, early symptoms can develop into periodontitis.
Early stages of gum disease can be seen with minor symptoms that include:
Red, swollen, or purple gums
Gums that feel tender to the touch
Bleeding gums
Chronic bad breath
Genetics
Some people are more susceptible to periodontal disease. Studies show that 30% of the population may be predisposed to gum disease, even if they take good care of their teeth.
Brushing too hard
If you brush your teeth too aggressively or incorrectly, it can cause your tooth’s enamel to wear away and your gums to recede.
Poor dental care
Inadequate brushing, flossing, and rinsing with antibacterial mouthwash, can make it easy for plaque to turn into tartar, a hard substance that forms on and between your teeth and can only be removed by a professional tooth cleaning.
Hormone levels
Changes in estrogen levels over a woman's life, like puberty, pregnancy, and menopause, can make gums increasingly sensitive and vulnerable to gum recession.
Tobacco products
Smokers, and other tobacco users, are more likely to develop sticky plaque which can cause gum recession.
Grinding and clenching your teeth
Clenching or grinding your teeth can exert too much force on the teeth, causing gums to recede.
Crooked teeth or a misaligned bite
When teeth don’t come together evenly, too much force can be exerted on the gums and surrounding bone, allowing gums to recede.
Receding Gums Treatment
Mild gum recession can be treated by a professional deep cleaning in the affected area. During the deep cleaning, plaque and tartar is removed and the exposed root area is smoothed over, making it more difficult for bacteria to attach itself. Antibiotics can also be used to kill any remaining bacteria.
If a deep cleaning is not sufficient to treat the condition, because of excess loss of bone and deep pockets, receding gums surgery may be required.
Questions About Receding Gums
Q: What causes your gums to recede?
A: There are a number of factors that can cause your gums to recede, including periodontal diseases. These are bacterial gum infections that destroy gum tissue and supporting bone that hold your teeth in place, which is the main cause of gum recession.
Q: How Can I Prevent Gum Recession?
A: Taking good care of your mouth is the best way to prevent gum recession. Brush and floss daily and see your dentist at least twice a year. Your dentist may want to see you more often If you have gum recession.
Quitting smoking, if you smoke.
Eating a healthy, well-balanced diet.
Monitoring possible changes to your mouth.
Q: How can I make my gums healthier?
Use an electric toothbrush.
Brush your teeth correctly, at least twice a day.
Use a toothbrush with a tongue scraper.
Floss daily.
Massage your gums.
Use a receding gums mouthwash and a receding gums toothpaste, with fluoride.

Sign Up
for expert advice and exclusive offers